All published articles of this journal are available on ScienceDirect.
Standardization and Detailed Aspects of Chopchinyadi Churna: A Potent Anti-Arthritic Medicine
Abstract
Background:
Chopchinyadi Churna is a powdered Ayurvedic churna, commonly used for treating insect bite, rheumatoid arthritis, gout arthritis.
Objective:
The current research is oriented for the evaluation of ingredients and other aspects of Churna.
Materials and Methods:
The Churna was standardized as per the parameters of Ayurvedic Formulary of India for the organoleptic characters, microscopy, physicochemical, chromatographic, rheological properties and phytochemical screening for the detection of major phytoconstituents.
Results:
The parameters were found to be significant and offered future benefits for the advanced evaluation of Churṇa.
Conclusion:
Herbal based anti-arthritic medicine Chopchinyadi Churna has been evaluated on the basis of various parameters, which can serve as references for developing the pharmacopoeial standards.
1. INTRODUCTION
Plants are the richest source of pharmaceutical lead molecules and their contribution to the drug discovery process is remarkable. Many herbs and herbal medicines have been used since time immemorial to cure many disorders/diseases, including arthritis [1]. In the traditional system of Indian medicine, combined extracts of individual plants are preferred rather than individual ones to achieve maximum therapeutic efficacy [2]. Nature has gifted us enormous wealth in the form of herbal plants, distributed all over the world as medicinal agents for the treatment of various diseases [3]. According to the WHO, 80% of the world’s population depends on herbal medicines for their primary health care requirements. Herbal medicines are irreplaceable and an important part of human society to combat diseases from a civilization [4].The medicinal properties of these herbal plants owe to the presence of chemical constituents that produce a desired physiological action on the body [5]. The preparation of a drug according to the ancient methods has minimized due to the commercialization of Ayurvedic pharmacy, therefore quality control is essential [6]. Chopchinyadi Churna is an Ayurvedic medicine, used in treating insect bite, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout, used commonly in North India [7]. Standardization of a herbal formulation is essential in order to ensure the quality, purity, safety and efficacy of the constituent drugs. Chopchinyadichurna is a polyherbal formulation comprising 11 ingredients i.e. madhusnuhi(smilax china), vidanga (embeliaribes), triphala, sugar, cinnamon,tvakpippali (piper longum), lavanga (clove), akarakarabha (Anacyclus pyrethrum), kokilaksha (Asteracanthalongifolia), marica (piper nigrum), and sunthi (Zinziberofficinale). Smilax china L. is known as chobchini in Hindi, madhusnuhi in Sanskrit and china root in English. It shows medicinal properties as being anti-inflammatory, diuretic, anti-diabetic, antipsoriatic, and digestive [8-11]. Embelia ribes Burm F., is also known as false black pepper or vidanga. It is a valuable medicinal plant exhibiting anthelmintic, carminative, antibacterial, antibiotic, hypoglycemic, and antifertility actions [12, 13]. All the other constituents of the formulation also have anti-arthritic potential. Though the contents of the formulation are rich enough to act against arthritis as most of them are potent anti-inflammatory agents. The present research focuses on the detailed aspects and complete standardization of Chopchinyadi churna composed of the constituents, which are used in the treatment of arthritic pains.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
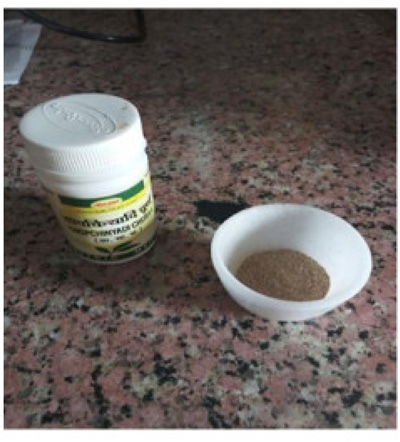
Chopchinyadi churna was procured as shown in Fig. (1) from the local market of Kanpur. It contains eleven ingredients, which are mentioned in Table 1. All of the constituents present act as potent anti-arthritic agents.

2.1. Role of Individual Constituents as an Anti-Arthritic Agent
2.1.1. Chopchini
Smilax chinensis, belonging to the family Liliaceae, actively acts as an anti-diabetic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer, analgesic, inflammation agent [14, 15]. The aqueous extract of Smilax china L. shows anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive activities [16].
2.1.2. Triphala
An Indian traditional Ayurvedic herbal formulation Triphala, which is composed of amla, bahera and harde has already been evaluated for the antiarthritic effect on adjuvant-induced arthritis in mice [17]. Triphala, containing Terminalia chebula Retz., Terminalia bellerica Roxb. and Emblica officinalis , is used for treating bowel-related complications, inflammations and gastritis [18]. Ayurveda doctors recommend this formulation to relieve symptoms of inflammatory joint problems like rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and gout [19].
| S.No | Herb | Botanical Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Chop chini | Smilax china |
| 2. | Sarkara | Sugar |
| 3. | Triphala | Emblica officinalis, Terminalia belerica, Terminalia chebula |
| 4. | Pippalimoola | Piper longum |
| 5. | Maricha | Piper nigrum |
| 6. | Lavanga | Syzigium aromaticum |
| 7. | Akarakarabha | Anacyclus pyrethrum |
| 8. | Kokilaksha | Asteracantha longifolia |
| 9. | Shunti | Zingiber officinalis |
| 10. | Vidanga | Embelia ribes |
| 11. | Cinnamon | Cinnamomum zeylanicum |
2.1.3. Pippali
The root of this plant is known as Pippali Mula in Ayurveda and its fruits found in the form of the spike are mainly used for Rasayana purpose. Several pharmacological activities like anti-ulcer, anti- amoebic, anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory activities have been reported for the fruit of this plant [20, 21].
2.1.4. Maricha
Maricha is also botanically known as piper nigrum.The main constituent of it is piperine, which shows anti- inflammatory, antinociceptive and antiarthritic effects.Black pepper or Piper nigrum is commonly used as a spice, but it also has multiple uses as a medicine, a preservative, and in perfumery. Its extract from the plant is rich in active phenolic component, piperine [22]. Its anti-inflammatory activities have been exhibited in rat models of carrageenan-induced paw edema [23]. Constituents of the piper species are responsible for in vitro inhibitory activity against the enzymes responsible for leukotriene and prostaglandin biosynthesis [24].
2.1.5. Clove
Clove contains essential oil, which possesses anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic properties [25]. At a lower concentration of 0.03% v/v, the anti-inflammatory activity of eugenol, which is the important constituent of its oil has been demonstrated in human gingival fibroblast and pulp cells [26, 27].
2.1.6. Akarakarabha
Anacyclus pyrethrum is widely used in Moroccan traditional medicine. It is active against inflammatory and painful diseases. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities have been exhibited by the aqueous and methanol extracts of roots of Anacyclus pyrethrum [28]. N-isobutyldienediynamide and polysaccharides are present in its roots [29-32]. It treats rheumatic arthritis by increasing circulation [33].
2.1.7. Asteracantha Longifolia
also known as askokilasha, helps in alleviating the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis [34]. It is rich in phytoconstituents as alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenoids, essential oil. It has been used in the traditional systems of medicine. Many pharmacological studies have been performed on the plant signifying its antioxidant and analgesic potential [35].
2.1.8. Zingiber Officinalis
Ginger is primarily known as curative [36]. It has also been used medicinally as an anti-inflammatory agent since antiquity [37-39]. Gingerols, the phenolic compounds are responsible for its pungent taste and usage in treating inflammatory disorders as arthritis [40]. The potent anti-arthritic effects of the extracts of ginger have been proven in an experimental model of rheumatoid arthritis. However, crude extracts containing both gingerols as well as essential oils have been found to be even more potent in inhibiting joint swelling as compared to gingerols alone [41].
2.1.9. Embelia Ribes
It is commonly known as Vidanga. It is used as a powerful anthelmintic in Ayurveda [42]. It has also been evaluated to have antifertility action [43]. Analgesic property has been reported for embelin and its derivatives [44]. It is used as an anti-inflammatory drug in the treatment of rheumatism and fever [45].
2.1.10. Cinnamomum Zeylanicum
Cinnamon is used for its aroma in the essence industries. Due to its fragrance, it is applicable for use in different varieties of foodstuffs, perfumes, and medicinal products [46]. Cinnamon bark is rich in ingredients as procyanidins and catechins [47]. The components of procyanidins include both procyanidin A and B [48-50]. Therefore it has been used as an anti-inflammatory agent [51-53].The major pharmacological uses of cinnamon bark are due to its anti-inflammatory and anti-microbial properties [54-57].
2.2. Phytochemical Screening
Plant extracts when tested for preliminary phytochemical screening, the presence of phytoconstituents as alkaloids, carbohydrates and reducing sugars, glycosides, proteins and amino acids, steroids and triterpenoids, tannins, flavonoids, fixed oils, volatile oils were detected. The methanolic extracts of the formulation were concentrated for further use.
2.3. Tests for Volatile Oils
The non-permanent staining of filter papers, along with the characteristic odour indicated the presence of volatile oils.
2.4. Tests for Alkaloids
Methanolic extracts of all the drugs were acidified and then filtered to obtain the filtrate to carry out further tests.
2.6. Tests for Carbohydrates and Reducing Sugars:
2.6.1. Molisch’s Test
To drug extracts, a few drops of alcoholic α-naphthol solution, followed by concentrated sulphuric acid were added. A purple ring at the junction of two liquids indicated the presence of carbohydrates.
2.6.2. Fehling’s Test
Fehling A and Fehling B solutions were mixed with equal volumes of the filtrates and heated for 5 minutes. First yellow, followed by brick red precipitate indicated the presence of reducing sugars.
2.8. Tests for Phenolic Compounds and Tannins
With 5% Ferric chloride solution, they gave a deep blue-black color [58, 59].
2.9. Organoleptic Evaluation
Dried powdered churna was taken in order to examine the macroscopic features of the formulation (Fig. 2). The morphological features were determined with the use of a simple microscope [60].

2.10. Microscopic Evaluation
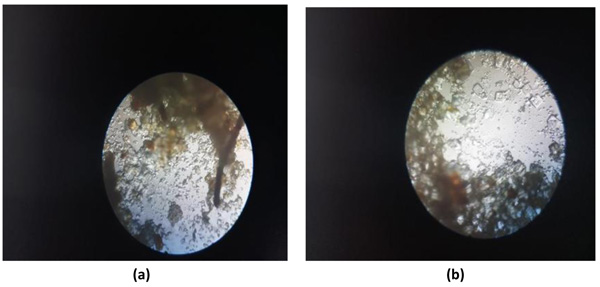
Coarsely powdered, air-dried samples were used for the purpose of microscopic evaluation. These were then treated with reagents like phloroglucinol and hydrochloric acid, followed by treatment with clearing agents, such as lactophenol and chloral hydrate in order to remove the impurities adhered. Then finally, they were mounted in glycerine. Glycerine, being an emollient, saves the sample from drying. Different cell components were studied as in Figs. (3a and 3b) per the standard methods with the help of different freshly prepared reagents [61-64].
2.11. Physico-Chemical Evaluation
Physicochemical standards as ash values, moisture content and extractive values were determined as per official methods and procedures.
2.12. Thin Layer Chromatography
A solvent system was used i.e toluene:ethyl acetate (9:3). Plates with the spotted sample were kept in the TLC chamber. Then, the chamber was closed with a lid. After spot development, the plates were removed and dried. Then sample spots were visualized in a UV light chamber (Fig. 4).
2.13. Rheological Evaluation
Coarsely powdered crude drug was screened for different parameters. Bulk density, angle of repose, compressibility, and Hausner’s ratio were calculated according to standard methods.
2.13.1. Bulk Density
10g of the powdered drug was taken in a graduated measuring cylinder and tapped on a wooden surface. Bulk density = weight taken / Bulk volume Tapped density = weight of drug taken / volume (tapped).
2.13.2. Angle of Repose
The angle of repose was determined by using the funnel method. The powderwas made to flow through a funnel fixed on a stand to form a heap. The height and the radius gave the angle of repose. The angle of repose tanθ = h/r θ = tan-1 (h/r). Where, h = height of heap, r = radius of the heap.
2.13.3. Compressibility / Carr’s Index
It is: Bulk density (Tapped) − Bulk density (Untapped)/ Bulk density (Tapped) Hausner’s Ratio. The formula used to determine Hausner’s ratio is Bulk density (Tapped) x 100 /Bulk density (untapped) [65, 66]. In spectral analysis, the churna was subjected to spectral techniques as Infra –red and ultraviolet spectroscopy [67-69].
3. RESULTS
Phytochemical analysis revealed the presence of alkaloid, tannins (due to the presence of amla, bahera, myrobalans in the form of triphala) reducing sugars, volatile oil (due to the presence of ginger, clove and piper species)and the absence of carbohydrate, saponins. It has been concluded that Churna is free from heavy metals. From the all above values, efficacy of the Churna is revealed (Table 2).
| S. No. | Chemical Tests | Reagents | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Test for Alkaloid | Hager’s Reagent | +ve |
| 2. | Test for Carbohydrate | Molisch Reagent | -ve |
| 3. | Test for Volatile oil | Filter paper | +ve |
| 4. | Test for Reducing Sugar | Fehling Sol. (A&B) | +ve |
| 5. | Test for Tannins | FeCl3 | +ve |
| 6. | Test for Saponin | Foam Test | -ve |
Botanical parameters revealed that Churna was light brown, moderately fine powder, odour- characteristic, taste- slightly sweet (Table 3).
| S.no | Parameter | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Colour | Light Brown |
| 2 | Odour | Characteristic |
| 3 | Taste | Slightly Sweet |
Results of quantitative analysis for loss on drying at 1050 C, total ash, acid insoluble ash, water soluble ash, alcohol soluble extractives and water soluble extractive were calculated and results are shown (Table 4). Ash value helps to assure the authenticity and purity of the drug. The loss on drying indicates the amount of moisture content present in the drug. Moisture content was found to be 8% w/w. The less value of moisture content prevents bacterial, fungal or yeast growth. The obtained values as water soluble and alcohol soluble indicate the amount of active constituent in the given amount of drug when extracted with the respective solvent. The Rf value was found to be 0.63.

| S.no | Parameter | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Moisture content | 8% |
| 2 | Total ash | 9.0% |
| 3 | Acid insoluble ash | 3.2% |
| 4 | Water soluble ash | 5.2% |
| 5 | Water soluble extractive | 41.5% |
| 6 | Alcohol soluble extractive | 11.5% |
| 7 | Rf Value | 0.63 |
Rheological properties of churnas shown in Table 5 like bulk density, tapped density, Hausner’s ratio and Carr's index indicate very poor flowability and the angle of repose indicates Poor-must agitate, with vibrate flow property.
3.1. Spectral Analysis of Churna
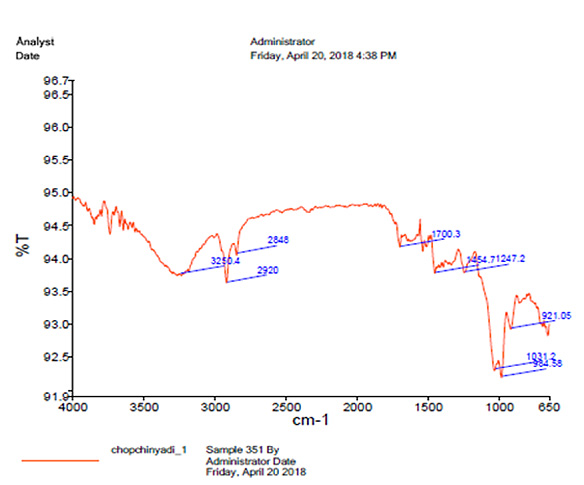
UV spectrophotometry revealed the absorbance 0.173 at 260 nm. Infrared spectroscopy revealed the presence of peaks at 1700 cm- and 3400 cm-, indicating the presence of keto and aldehyde groups containing phytoconstituents in the formulation (Fig. 5).
4. DISCUSSION
Phytochemical screening of churna showed the absence of carbohydrates and saponins. It revealed the presence of tannins, reducing sugars, volatile oil and alkaloids. Morphology discussed the light brown, slightly sweet taste of it. The moisture content was found to be 8% w/w. The less value of moisture content prevents bacterial, fungal or yeast growth. The extractive values as water soluble and alcohol soluble indicate the amount of active constituent in the given amount of drug when extracted with the respective solvent. Powder on its flow study showed that it has a very poor flowability and the angle of repose indicates poor must agitate, with vibrate flow property. Spectral analysis indicated the presence of keto and aldehyde groups containing phytoconstituents in the formulation [70, 71].
CONCLUSION
Various evaluation parameters like physicochemical standards as total ash, acid insoluble ash, water and alcohol-soluble extractive values, loss on drying, microscopy, spectroscopy, phytochemical analysis, flow properties, and morphological features were evaluated. From their results, it was revealed that the formulation of Churna is effective with uniform characteristics of an ideal Churna. It is beneficial, effective and economic as well. The efficacy of the Churna can be proved by the pharmacology which suggests the future scope of R & D. Though the contents of the formulation are rich enough to act against arthritis as most of them are potent anti-inflammatory agents. The study shows that the ingredients of churna presentare in accord with the prescribed guidelines of the WHO. All these observations are not mentioned in the standard literature, which could be helpful in authentication and assurance of Churnas. The result of the present study will help to set standards as a reference monograph in the process of drug formulation. Ayurvedic Churna has been standardized by the intervention of modern scientific quality control measures in the traditional preparation described in classical texts. Pharmacognostic characters established for the raw materials could be employed as Q.C. standards for evaluating cccstheir identity and can be used for routine analysis.
| S.no. | Parameter | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tapped density | 40.2 |
| 2 | Untapped density | 33.4 |
| 3 | Angle of repose | 33.5 |
| 4 | Hausner ratio | 1.2 |
ETHICAL APPROVAL AND CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE
Not applicable.
HUMAN AND ANIMAL RIGHTS
No animals/humans were used for studies that are the basis of this research.
CONSENT FOR PUBLICATION
Not applicable.
AVAILABILITY OF DATA AND MATERIALS
The authors confirm that data supporting the findings of this research are available within the article.
FUNDING
None.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Declared none.


